Ultrasound method enables easier disease diagnosis
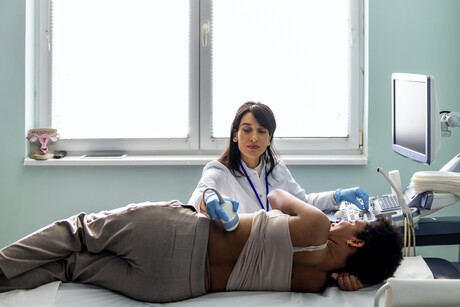
Researchers from the University of Sheffield have developed a new ultrasound method that can measure the level of tension in human tissue for the first time — a key indicator of disease. The breakthrough by Sheffield’s Dr Artur Gower, together with researchers from Harvard Medical School, Tsinghua University and the University of Galway, could be used to build new ultrasound machines that are able to better diagnose abnormal tissue, scarring and cancer.
Ultrasounds use sound waves to create images of organs inside the human body. However, the images produced by the current techniques used in health care aren’t usually enough to diagnose whether tissues are abnormal. To improve diagnosis, the researchers developed a way to measure forces such as tension by using an ultrasound machine. Tension is generated in all living tissue, so measuring it can indicate whether tissue is functioning properly or if it’s affected by disease.
The researchers harnessed a technique from a rail project at the University of Sheffield, which uses sound waves to measure tension along railway lines. The technique, used both for rail and medical ultrasound, relies on a simple principle: the greater the tension, the faster sound waves propagate. Using this principle, the researchers developed a method that sends two sound waves in different directions. The tension is then related to the speed of the waves by using mathematical theories developed by the researchers.
Previous ultrasound methods have struggled to show the difference between stiff tissue or tissue under tension. The new technique is said to be the first capable of measuring tension for any type of soft tissue, without knowing anything about it. The researchers described the technique in the journal Science Advances and how they used it to measure tension inside a muscle.
“When you go to the hospital, a doctor might use an ultrasound device to create an image of an organ such as your liver, or another part of your body, such as the gut, to help them explore what the cause of a problem might be,” Gower said. “One of the limitations of ultrasounds used in health care now is that the image alone is not enough to diagnose whether any of your tissues are abnormal.
“What we’ve done in our research is develop a new way of using ultrasound to measure the level of tension in tissue. This level of detail can tell us whether tissues are abnormal or if they are affected by scarring or disease. This technique is the first time that ultrasound can be used to measure forces inside tissue, and it could now be used to build new ultrasound machines capable of diagnosing abnormal tissue and disease earlier.”
A non-destructive way to locate microplastics in body tissue
Currently available analytical methods either destroy tissue in the body or do not allow...
Rapid imaging method shows how medicine moves beneath the skin
Researchers have developed a rapid imaging technique that allows them to visualise, within...
Fluorescent molecules glow in water, enhancing cell imaging
Researchers have developed a new family of fluorescent molecules that glow in a surprising way,...




