Australia and China partner on fusion energy research
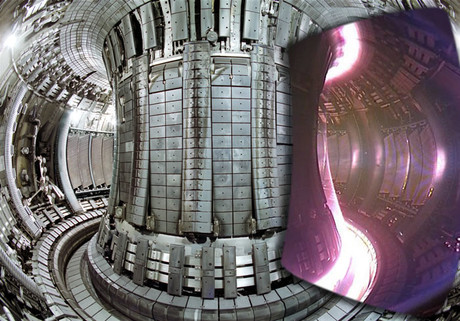
The Australian National University (ANU) and the University of South China (USC) have agreed to work together on fusion energy research, with the prospect of Australia providing China with its first plasma stellarator device.
Nuclear fusion, which powers our sun and all stars in the universe, has the potential to provide sustainable, zero-emission and relatively cheap power to grids. Now, after years of funding support from the Australian Government, ANU has developed strong technical expertise in a type of plasma fusion device called a stellarator — one of the two fusion devices that are most likely to be viable power sources.
Signing a memorandum of understanding (MoU) this week, Australia and China formalised their new fusion research relationship, which is likely to see Australia provide China with its first stellarator device. According to Dr Cormac Corr, director of the Australian Plasma Fusion Research Facility at ANU, the MoU serves as an important step towards developing a future energy source for the world.
“Australia will benefit from enhanced national investment, and for China the relationship will form the core of China’s first stellarator program,” he said.
“The agreement will be finalised in the next few months and will start with significant exchange of technical and academic personnel between the two institutions.”
Dr Corr revealed that ANU is currently working towards making fusion a viable baseload power source by 2050. He stated, “Australia working closer with China on this technology will help to make this a reality.”
Colon cancer DNA in blood can guide chemo decisions
A simple blood test could change how doctors decide which patients with colon cancer need...
Non-invasive blood test helps rule out oesophageal cancer
Designed and developed in Australia, the PromarkerEso test is designed to offer a quick,...
Taste-based flu test enables rapid diagnosis
The diagnostic tool consists of the sensor molecule thymol and a virus-specific sugar building...



